SKIN CARE
Skin is the body’s largest organ and acts as an external barrier to microorganisms and extreme environmental conditions. There are numerous conditions that can affect the skin, preventing you from looking and feeling your best. Two of the most common of these are acne and aging skin.
ACNE
Acne develops as a result hair follicles that become plugged with oil and dead skin, leading to pimples. Contributing factors to the development of acne includes excessive oil production and hormones (androgenic hormones). Severe acne, if not properly treated, can lead to facial pitting, scarring, and lose of self-esteem.
Acne can typically be well managed with consistent hygiene. A sample Daytime Regimen is provided below. We may also suggest various treatments, hydration techniques and nutritional supplements to maintain and improve your skin’s elasticity and health.
Your Daytime Regimen
Step 1: CLEANSER. In the morning, start by splashing your face with warm water, or wash with a gentle face cleanser designed for your skin type.
Step 2: TONER. Apply toner after cleansing to balance pH and reduce pore size, effectively minimizing penetration of impurities and environmental contaminants.
Step 3: ANTIOXIDANT SERUM. Neutralize free radicals to prevent further damage to your skin. Antioxidant serum can lead to more radiant skin, reduce acne scarring, even out skin tone, soften wrinkles.
Step 4: MOISTURIZER. A layer of oil-free moisturizer boosts skin hydration and creates a protective layer of moisture.
Step 5: SUNSCREEN. Lastly, add a layer of sunscreen to reduce the risk of skin cancer and photoaging.

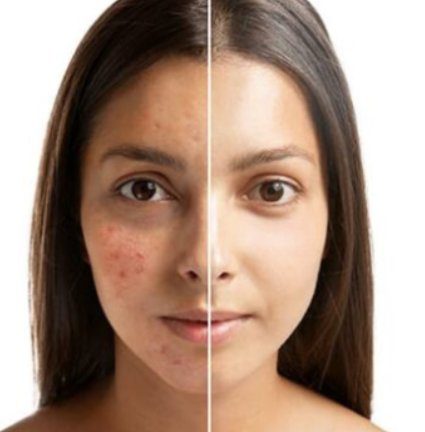
ACNE TREATMENT
Acne symptoms can include whiteheads, blackheads, small red tender pumps(papules) or large painful lumps beneath the skin. Although in severe cases a prescription cleanser or medication may be needed. After trying the below cleaning tips if no considerable improvement is observed, it may be time to explore other treatments options.

Nonprescription Treatment for Acne
SOAP AND WATER: Gentle cleansing of the face with soap and water no more than two times a day can help with acne. However, this does not clear up acne that is already present. Aggressive scrubbing can injure the skin and cause other skin problems.
CLEANSERS: There are many cleansers and soaps advertised for treating acne. They often contain benzoyl peroxide, glycolic acid, salicylic acid, or sulfur.
BENZOYL PEROXIDE: For mild acne, you may try, or your doctor may recommend, treatment with a nonprescription drug that contains benzoyl peroxide. It’s believed that this compound works by destroying the bacteria associated with acne. It usually takes at least four weeks to work and it must be used continuously to keep acne at bay. Like many over-the-counter and prescription products, it does not affect sebum production or the way the skin follicle cells are shed, and when you stop using it, the acne comes back. It is available in many forms: creams, lotions, washes, foams, cleansing pads and gels. Benzoyl peroxide can cause dry skin and can bleach fabrics, so take care when applying it. Consider wearing an old T-shirt to bed if you are applying it to your back or chest overnight.
SALICYLIC ACID. On the skin, salicylic acid helps to correct the abnormal shedding of cells. For milder acne, salicylic acid helps unclog pores to resolve and prevent lesions. It does not have any effect on sebum production and does not kill bacteria. It must be used continuously, just like benzoyl peroxide, because it effects stop when you stop using it – pores clog up again and the acne returns. Salicylic acid is available in many acne products, including lotions, creams, and pads.