OVERVIEW ON URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection in any part of your urinary system including your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Most infections involve the lower urinary tract which is the bladder and the urethra.
Women are at greater risk of developing a UTI than are men. Infection limited to your bladder can be painful and annoying. However, serious consequences can occur if a UTI spreads to your kidneys.
Doctors typically treat urinary tract infections with antibiotics. But you can take steps to reduce your chances of getting a UTI in the first place.
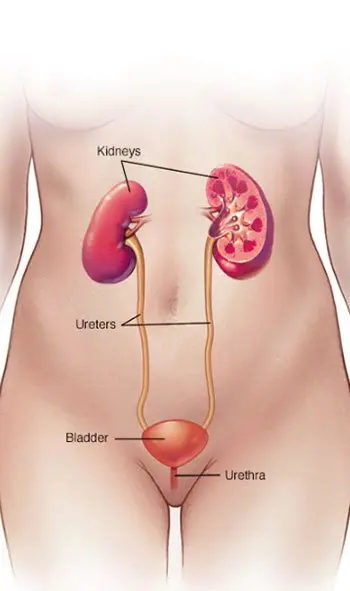
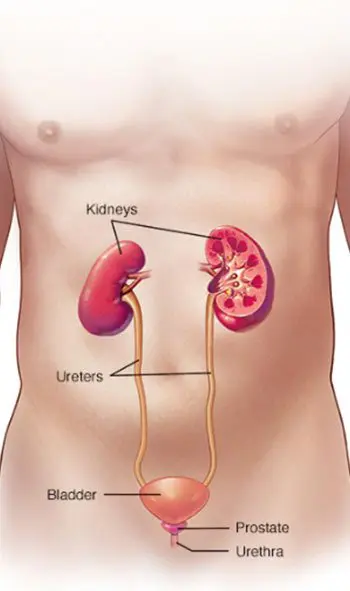
Urinary tract infections don’t always cause signs and symptoms, but when they do, they may include.
- A strong, persistent urge to urinate
- A burning sensation when urinating
- Passing frequent, small amounts of urine
- Urine that appears cloudy
- Urine that appears red, bright pink or cola-colored – a sign of blood in the urine.
- Strong-smelling urine
- Pelvic pain, in women – especially in the center of the pelvis and around the area of the pubic bone.
UTIs may be overlooked or mistaken for other conditions in older adults.
TYPES OF URINARY TRACT INFECTION
Each type of UTI may result in more-specific signs and symptoms, depending on which part of your urinary tract is infected.
- Upper back and side (flank) pain
- High fever
- Shaking and chills
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Pelvic pressure
- Lower abdomen discomfort
- Frequent, painful urination
- Blood in urine
- Burning with urination
- Discharge
CONTACT US IF YOU HAVE SIGNS OR SYMPTOMS
When treated promptly and properly, lower urinary tract infections rarely lead to complications. But left untreated, a urinary tract infection can have serious consequences.